
What's New In Speak - April 2024
Interested in What's New In Speak February 2024? Check out this post for all the new updates available for you in Speak today!
In recent years, large language models (LLMs) have become increasingly popular tools for natural language processing (NLP) tasks such as sentiment analysis, text summarization, and question-answering.
These powerful models are capable of capturing complex linguistic relationships between words and are being used in a variety of ways to improve the accuracy and efficiency of NLP tasks.
In this article, we’ll explain what large language models are and how they work. We’ll also discuss the advantages and disadvantages of using these models and provide some examples of their applications. We've also created a dedicated article on what are language models.
Large language models (LLMs) are a type of deep learning model that is used to learn and make predictions about natural language. These models are trained on large amounts of text data, such as books, news articles, and social media posts, and are designed to capture complex relationships between words and phrases.
LLMs are typically trained using a technique known as “transfer learning” where a pre-trained model is adapted to a specific task by fine-tuning the weights of the model. This allows the model to better capture the nuances of the task at hand. The most commonly used type of LM is the “recurrent neural network” (RNN) which is a type of artificial neural network that is designed to process sequential data.
Large language models work by taking in large amounts of text data and using that data to learn the relationships between words and phrases. These models are trained using a technique known as “transfer learning” where a pre-trained model is adapted to a specific task.
The training process begins with a “corpus” of text data which is a collection of documents that contain the language that the model will be trained on. The model is then trained on this corpus of text data in order to learn the relationships between words and phrases.
Once the model has been trained, it can be used to make predictions about new text data. This is done by feeding the model a new sentence or phrase and having the model predict the most likely words that come next in the sequence. This process can be used to generate new text or to analyze existing text for sentiment and meaning.
Large language models offer several advantages over traditional NLP models. For instance, they are capable of capturing complex relationships between words and phrases which can lead to more accurate predictions. Additionally, these models can be trained on large amounts of data which allows them to learn the nuances of a language quickly and accurately.
However, there are also some drawbacks to using large language models. These models require a large amount of computing power which can be expensive and time-consuming. Additionally, these models can be difficult to interpret which can lead to unexpected results.
Most of us who are interested in large language models have seen crazy outputs that are being shared on Twitter, Reddit forums and other social media platforms. For example, Microsoft famously had a chatbot on Twitter that became racist in less than a day.
Large language models are being used in a variety of ways to improve the accuracy and efficiency of NLP tasks. Some of the most common applications include:
We’ve seen explosions of text generation functions within large language models from companies like OpenAI, Jasper, and Copy Ai.
We’ve also seen a rampant increase in the application of text-to-image generation from companies like Stability Ai, Midjourney, OpenAI and more.
Large language models can be used to generate summaries of text documents or articles. These summaries can be used to quickly read and understand large amounts of text.
Large language models can be used to generate accurate answers to questions posed in natural language. This can be used to create chatbots and other AI-driven customer service systems.
Large language models can be used to analyze text data and accurately determine the sentiment of the text. This can be used to understand customer feedback and improve customer experience.
Large language models can be used to generate captions for images. This can be used to improve the accuracy of image recognition systems.
Large language models are powerful tools for natural language processing tasks. These models are capable of capturing complex relationships between words and are being used in a variety of ways to improve the accuracy and efficiency of NLP tasks.
In this article, we’ve explained what large language models are and how they work. We’ve also discussed the advantages and disadvantages of using these models and provided some examples of their applications.
If you are interested in learning more about large language models, you can also check out our article on the best large language models.
Get a 7-day fully-featured trial.
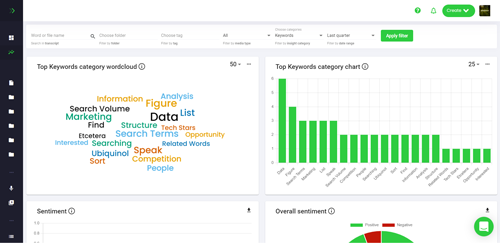

Interested in What's New In Speak February 2024? Check out this post for all the new updates available for you in Speak today!

Interested in What's New In Speak February 2024? Check out this post for all the new updates available for you in Speak today!
Interested in What's New In Speak February 2024? Check out this post for all the new updates available for you in Speak today!

Thank you for continuing to be part of this journey - it means the world to us. Below is a summary of our 2023 at
Interested in The Best Executive Research Firms? Check out the dedicated article the Speak Ai team put together on The Best Executive Research Firms to learn more.

Interested in The Best Consumer Research Firms? Check out the dedicated article the Speak Ai team put together on The Best Consumer Research Firms to learn more.

Powered by Speak Ai Inc. Made in Canada with
Use Speak's powerful AI to transcribe, analyze, automate and produce incredible insights for you and your team.