Measuring and improving our impact on the world.
This dedicated page on impact reporting for Speak Ai has been made to measure, improve and share our progress in regard to sustainability.
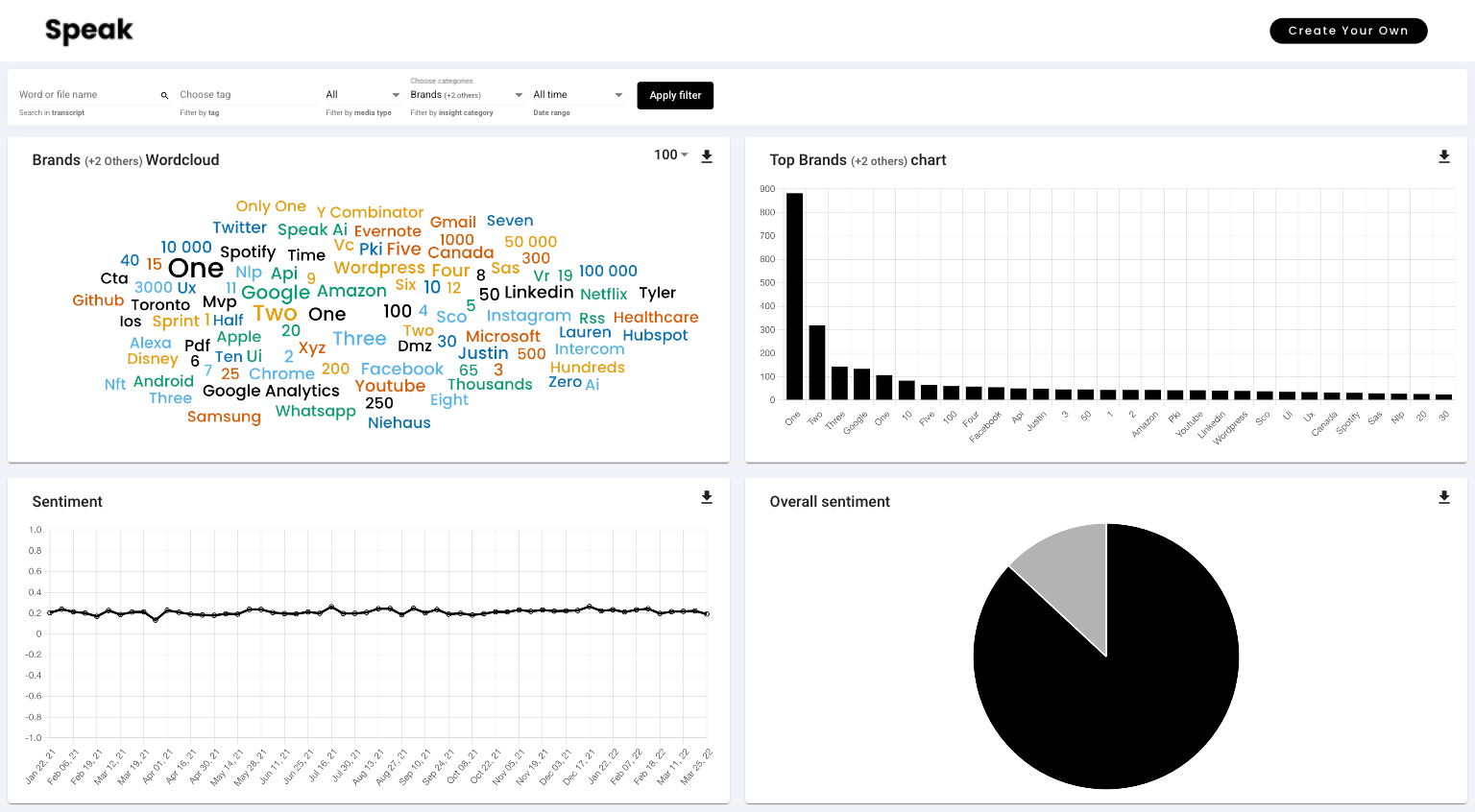



































Speak Ai builds and uses incredible speech recognition and natural language processing technologies to help over 20,000 users derive meaningful insights from their language data.
While we are proud of our system's capabilities, we also recognize the intense computational power and therefore energy our system uses.
Below, we document the energy we have been able to calculate across all of our systems. We are continuously trying to improve our understanding of energy and environmental impact and will update this page with information.
As we measure our impact, we also look for ways to improve it. Speak Ai is already deploying several techniques to mitigate our environmental impact.
As just one example, Speak Ai uses a clustering system of servers that only activates based on usage and then scales back when it is unused to reduce energy and server loads.
Additionally, we specifically choose cloud providers that have made commitments to positive environmental impact and have measures to retrieve related data so we can understand our own impact.
The i.d.e.a. Fund supports a more sustainable economy and equitable recovery in Southern Ontario by providing recipients with $30,000 in matching seed funds and up to 40 hours of expertise from our Venture Growth team.
The i.d.e.a. Fund is delivered in partnership with the following Ontario Regional Innovation Centres: Innovation Guelph, Haltech, Innovate Niagara, WEtech Alliance, TechAlliance of Southwestern Ontario, and Innovation Factory.
i.d.e.a. Fund is funded by the Government of Canada’s Jobs and Growth Fund, which advances economic recovery efforts, supports businesses and organizations to help create jobs, supports the transition to a green economy, and positions local economies for long-term growth.

We hook into every service we use, including Amazon Web Services, MongoDB, Microsoft Azure, and more, to identify and aggregate the usage to accurately represent our energy consumption and environmental impact.
Amazon Web Services is one of the largest cloud computing platforms, serving millions of businesses and organizations worldwide. However, AWS also has a substantial carbon footprint, with estimates indicating that its data centers generate approximately 60 million metric tons of CO2 annually. Despite this, AWS has committed to reaching net-zero carbon emissions by 2040 and has launched several initiatives to achieve this goal. These include investing in renewable energy, optimizing its infrastructure to reduce energy consumption, and partnering with customers to reduce their carbon footprints.
It has created a separate tool within a platform to track, measure, review, and forecast the carbon emissions generated from AWS usage. AWS usage is summarized under two categories:
We have near to 0 Carbon emissions calculated on our AWS account.
MongoDB, as a software company, produces limited carbon emissions. The vast majority of their carbon footprint is attributable to emissions related to their value chain.
The most significant contribution comes from their cloud partners' data centers, including Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud. We have deployed our database on one of the cloud providers. Their efforts to reduce carbon footprints automatically reduce MongoDB's carbon footprint. [Source: MongoDB Sustainability Report]
Additionally, MongoDB offers its customers tools to help them reduce their carbon footprints by optimizing their database queries and improving their application code.
Microsoft Azure is another leading cloud computing platform serving businesses and organizations across the globe. Like AWS, Azure has a significant carbon footprint, with estimates indicating that its data centers generate approximately 44 million metric tons of CO2 annually. However, Azure has also committed to achieving net-zero carbon emissions by 2030, ten years ahead of AWS's target. Azure is investing in renewable energy, improving its data center efficiency, and developing new technologies to help its customers reduce their carbon footprints to achieve this goal.
Azure has developed a proprietary tool called the Carbon Reduction Dashboard, enabling the company to monitor and analyze its carbon emissions continuously. This dashboard provides Azure with real-time data on energy consumption, carbon emissions, and the environmental impact of its operations. By tracking its carbon footprint meticulously, Azure can identify areas where it can reduce its emissions and make informed decisions about where to invest in carbon reduction measures.
It requires various access and installation of the application to understand the emission usage.
Get a 7-day fully-featured trial.


Powered by Speak Ai Inc. Made in Canada with
Use Speak's powerful AI to transcribe, analyze, automate and produce incredible insights for you and your team.